Interactive notebooks offer a flexible environment for combining code, text, and visualisations, making them a widely used tool for exploratory data analysis and reproducible research. Within FAIR-EASE, two platforms are supported:
JupyterLab, mainly used by data scientists, which is compatible with numerous languages (e.g. Python, R, Julia) and provide a lot of extensions ;
Pluto.jl, dedicated for Julia programmers, which provides a reactive environment.
A special focus is placed on JupyterGIS, a new approach for collaborative geospatial analysis within notebooks. It combines the flexibility of Jupyter with tools tailored for GIS operations and visualisation, enabling users to explore spatial data, apply processing functions, and share results, all within a unified interface designed for collaborative use.
In order to promote the integration and use of cloud-based object storage systems, particularly through the use of an S3 backend.
Tutorial notebooks have been designed and shared (https://
- manipulation of elements (buckets, objects, rights).
- interaction (adding, deleting)
and how to use this type of storage in pipelines: - file format conversion (native to cloud-optimised to improve access and processing speed)
- data transformations (columns, aggregation)
- data selection based on criteria
- interaction with third-party tools
- automatic file generation
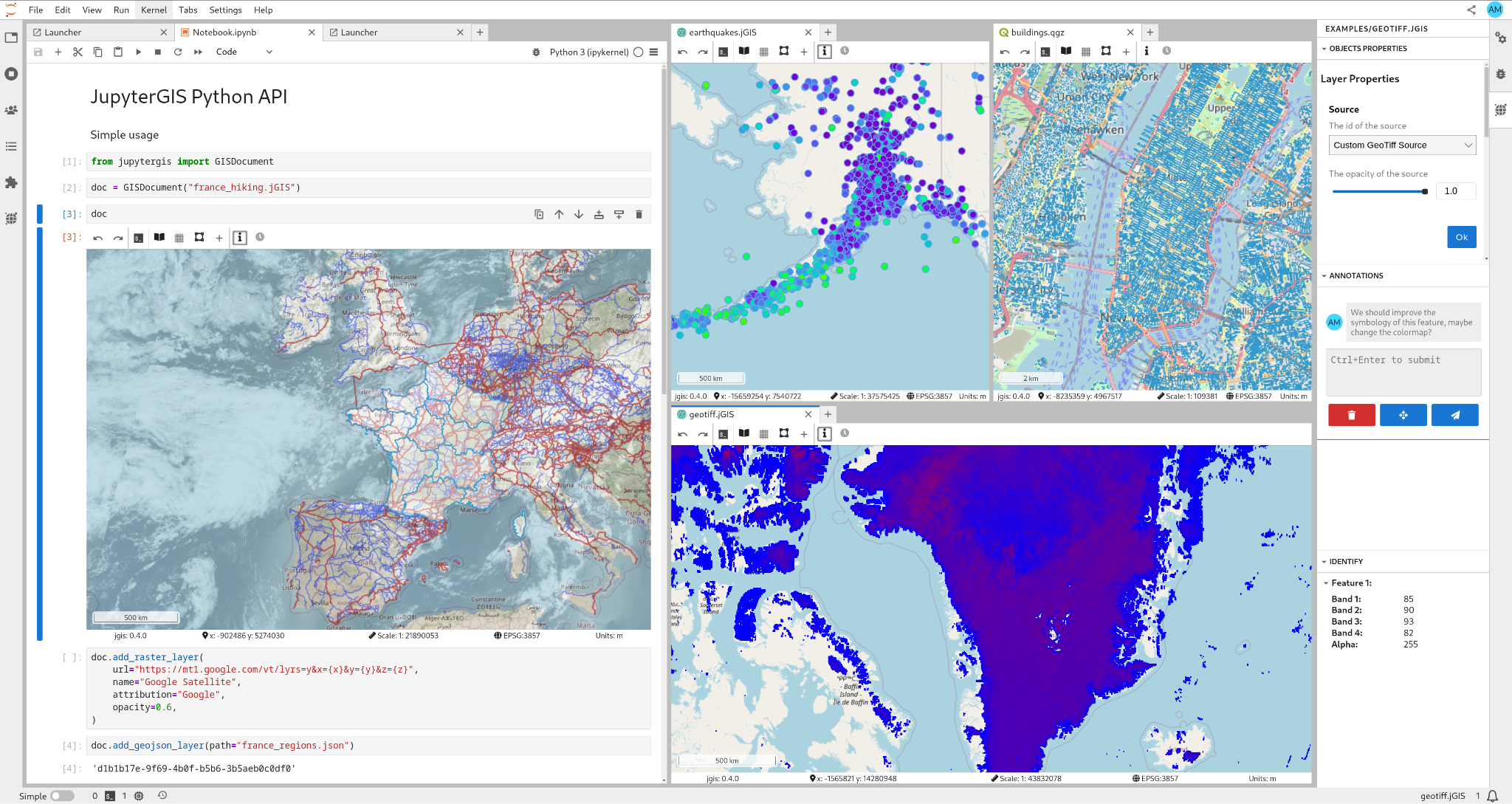
Figure 1:JupyterGIS[25] (source: https://