EMO-BON¶
The European Marine Omics Biodiversity Observation Network (EMO BON) is an initiative of the European Marine Biological Resource Centre (EMBRC) to establish a persistent genomic observatory among designated European coastal marine sites. All stations share the same protocols for sampling and undergo the same data curation to maximise comparability among sites and through time. Environmental samples are collected from the water column, and at some sites, soft sediments and hard substrates (Autonomous Reef Monitoring Structures - ARMS), together with a set of mandatory and discretionary metadata (including Essential Ocean Variables - EOVs). Samples are collected following specified protocols at regular and specified intervals, and sequenced in large six-monthly batches at a centralised sequencing facility. The use of standard operating procedures (SOPs) during data collection, library preparation and sequencing aims to provide uniformity among the data collected from the sites; coupled with strict adherence to open and FAIR data principles, the SOPs ensure maximum comparability among samples, and enhance reusability and interoperability of the data with other data sources. The observatory network was launched when the first sampling campaign took place, in June 2021.
MetaGOflow Workflow Analysis¶
All EMO BON metagenomic samples are analysed with the sample analytical workflow constructed specifically for the project called MetaGOflow (MGF, GitHub, article). MGF is based on the “reads” subworkflow of the EMBL-EBI MGnify workflow (v.5) from which it was derived, and performs raw sequence curation, sequence assembly, and taxonomic and functional annotation based on the read sequences.
Data Management¶
A typical MGF analysis produces approximately 25GB of data products that are packaged in specialised RO-Crates with the actual data files being stored in an S3 object store. Both the MGF data and the metadata describing the EMO BON sampling events are contained in an RDF triple store. RO-crate contents can be visually inspected using a RO-crate viewer deployed at data
TripleStore¶
The TripleStore harvests the RDF triples from the RO-Crates into a graphDB database accesible via a SPARQL endpoint.
Uniform Data Access Layer (UDAL)¶
UDAL provides agnostic aproach to qury data from diverse sources using pre-defined named queries. In the context of FAIR-Ease and EMO-BON data, UDAL is implemented in python and queries target SPARQL endpoint. For details on UDAL itself, please refer to the documentation, named queries specifications and dataset demand registry examples.
Data Catalogue¶
IDDAS (Interdisciplinary Data Discovery and Access Services): This metadata catalogue leverages existing data catalogues, modeled along a tuned FAIR-EASE DCAT Application Profile. By utilising RDF metadata descriptions for semantic web compatibility, the IDDAS allows users and systems alike to search, discover, and access Earth System data seamlessly. The IDDAS uses both human and machine-readable formats, thereby ensuring accessibility across various platforms within, and between, data spaces.
The IDDAS uses a DCAT metadata profile, those metadata are fed by the EMO BON RDF metadata triple store to find the dataset records for each of the EMO BON RO-Crates: the logsheet RO-Crates (containing sample data) and the MFG RO-Crates (containing the bioinformatics data and analyses outputs).
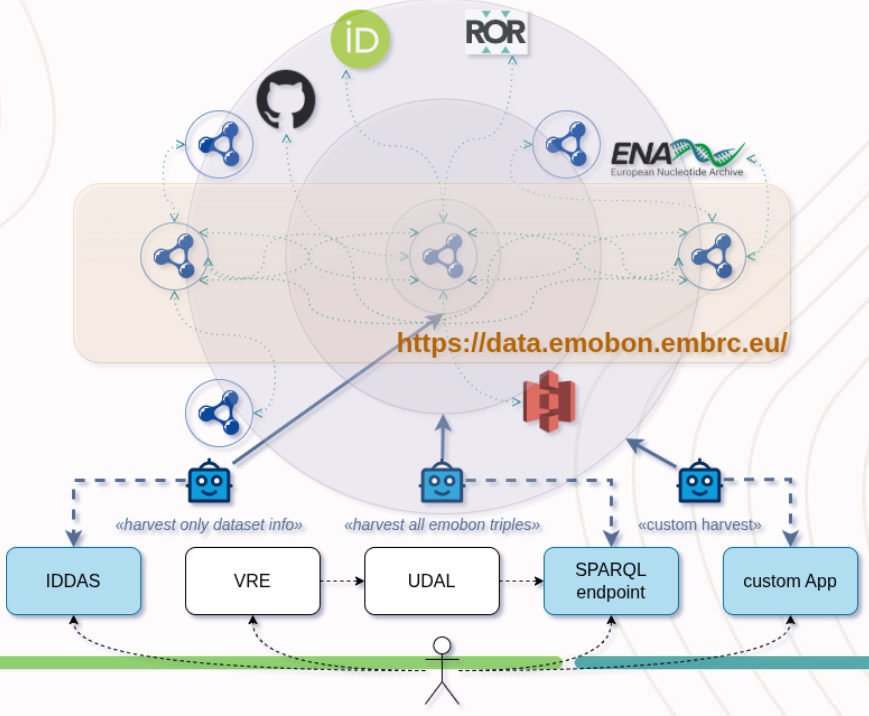
Figure 1:Marine Omics Pilot architecture, credits Marc Portier.
EMO-BON data analysis kit (DAK)¶
DAK provides basic research tools to interogate, visualize and analyse EMO-BON data queried with UDAL. Some have visual interface as a dashboard served from the Jupyter notebook or alternatively without the dashbord component as Jupyter notebook alone.
Thorough description of the DAK follows in the next chapter EMO-BON data analysis kit.
Virtual Research Environment¶
The full flaged integration of the DAK with access to IDDAS and Galaxy instance is planned for fall 2025 as a VRE prototype on D4Science (BlueCloud infrastructure). In the VRE, it will be possible to leverage both UDAL queries or IDDAS search to retrieve the data.
Details of the VRE are described in chapter Virtual Research Environment