The Spatio-Temporal Assets Catalog[8] (STAC) is a standardised model and API for geospatial data indexing and discovery. It provides a lightweight yet powerful framework for organising and exposing data inventories, whether native (e.g. NetCDF, Tiff) or ARCO (e.g. COG, Zarr, Geoparquet).
STAC is structured hierarchically, and is based on the HATEOAS[9] principle, enabling navigation between these elements. Here are the main concepts:
Collection: represents a logical grouping of related data (for example, a sensor, a mission or a family of datasets)
Item: describes a single observation or spatio-temporal scene, such as a satellite image or an in situ measurement campaign
Asset: data or metadata files accessible via URLs
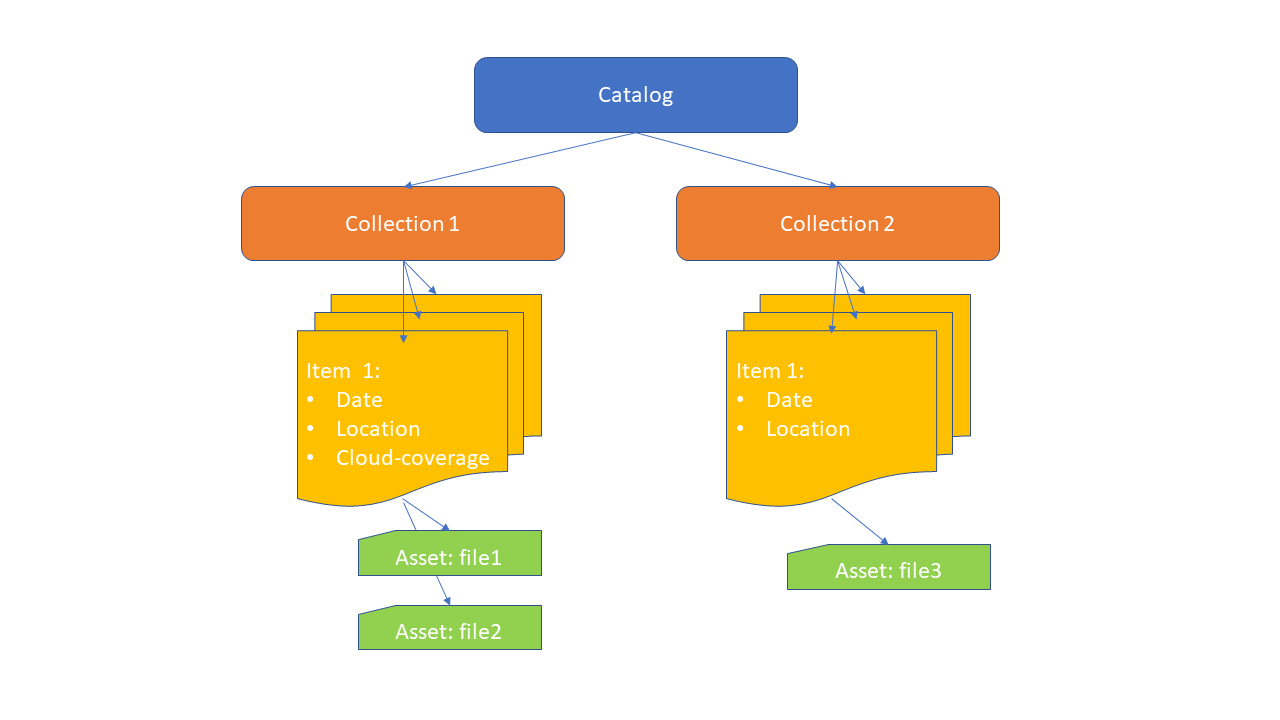
Figure 1:STAC Schema
STAC offers rich search capabilities based on spatio-temporal criteria, extended with additional filters using CQL2 (e.g. observed parameter). This enables users and applications to discover relevant items and directly retrieve the corresponding assets from distributed or cloud infrastructures.
Originally developed for earth observation satellite images, FAIR-EASE has extended its use to in situ data, taking care to provide rich metadata, with as many links as possible to controlled vocabularies.
Here is the architecture proposed by FAIR-EASE:
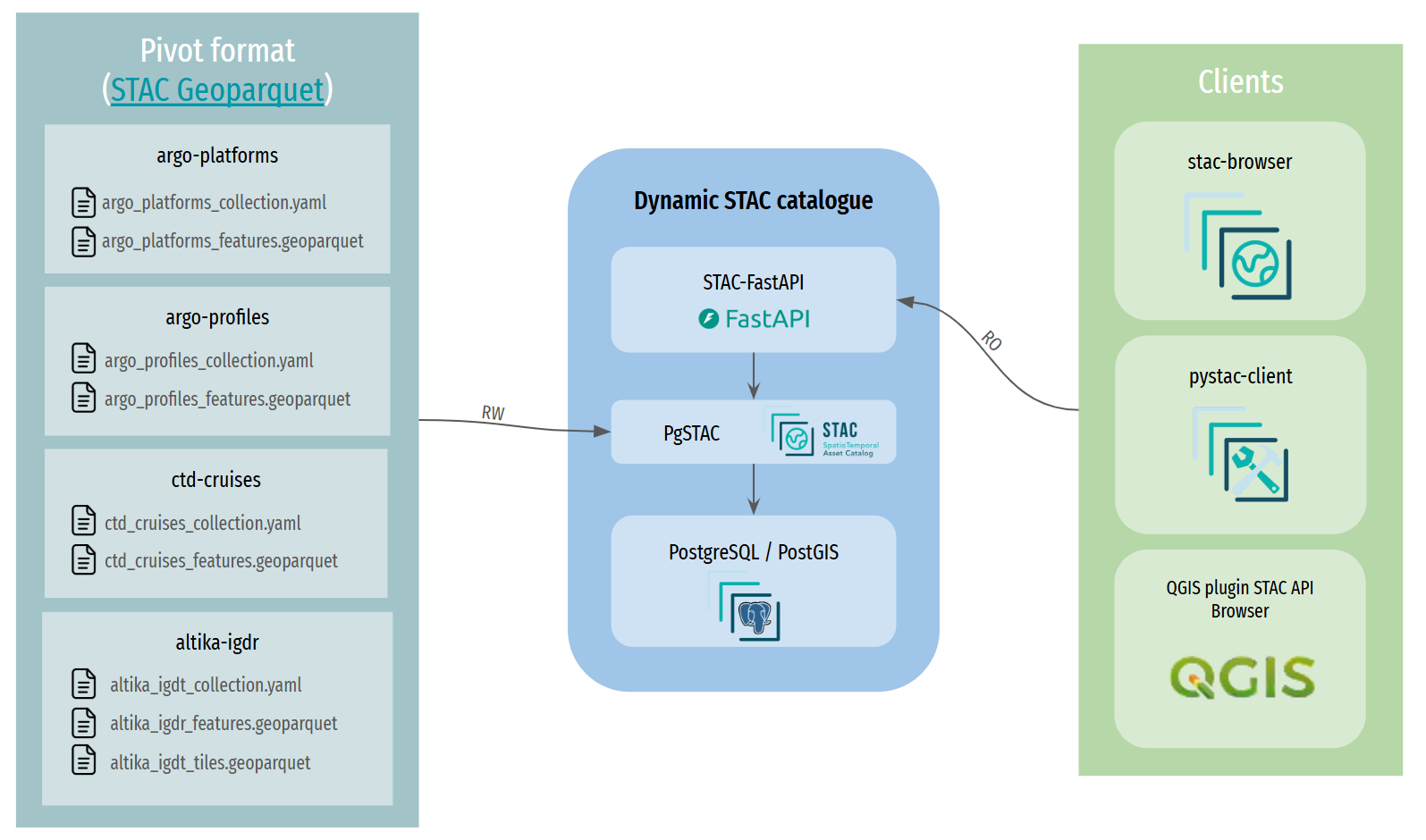
Figure 2:STAC architecture
An implementation has been provided by Ifremer to demonstrate the use of
STAC for in-situ data, including native ARGO datasets. This includes a
public STAC API available at
[stac
Here is a screenshot of an ARGO profile item from the STAC Browser:
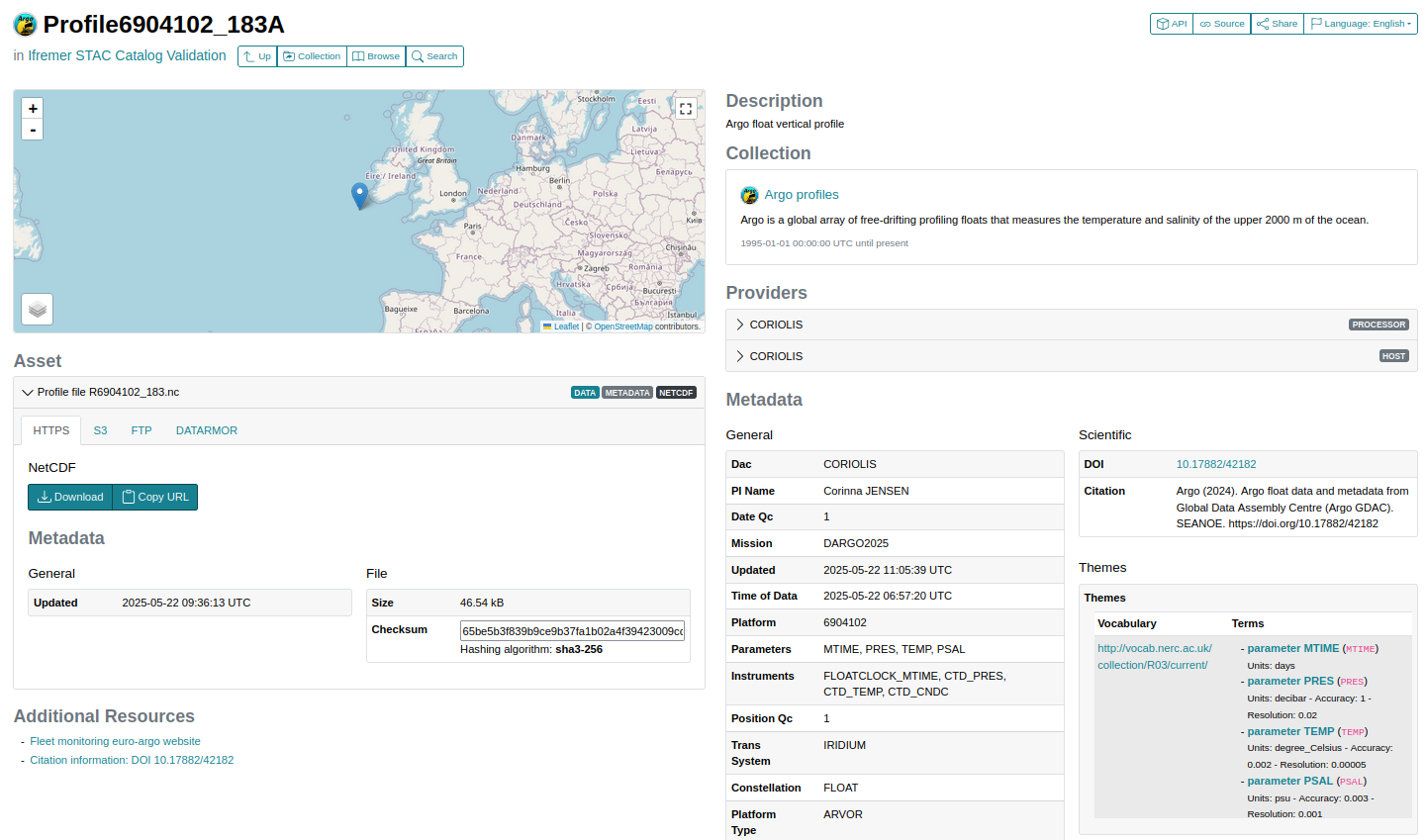
Figure 3:STAC Browser example